Kilauea, an erupting volcano in Hawaii
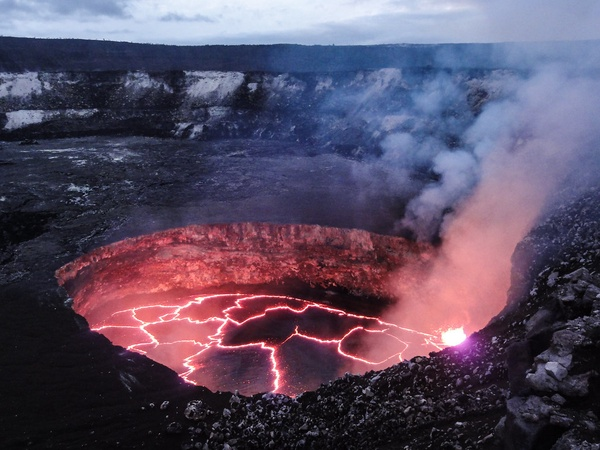

Photo courtesy of U.S. Geological Survey Department of the Interior/USGS
November 12, 2021
Hawaii’s volcano Kilauea, is currently spewing lava, and the lava lake on the volcano has been expanding ever since the eruption. The lake is becoming dangerously close to overflowing and spreading towards towns.
Kilauea began erupting on Sept. 29 at 3:45 p.m. The volcano hasn’t shown any signs of stopping as far as experts are aware. During the eruption, H2O, Co2, and So2 were released into the air. So2 being released from the summit and shooting into the atmosphere has created vog (volcanic fog) and has been observed moving down the mountain towards more densely populated areas, which would lead to dangerous outcomes. The vog creates dangerous and deadly results. With the volcano being more active ever since 1924, Kilauea has become much more dangerous. The lava from the volcano hasn’t slowed down its flow, but luckily scientists have been able to contain some of the flow from reaching the populated areas and having deadly consequences.
“Stay inside and avoid any exposure to ash” prompts the USGS. According to the USGS website, vog can lead to airborne health hazards. It can also damage crops and plants in the surrounding area.